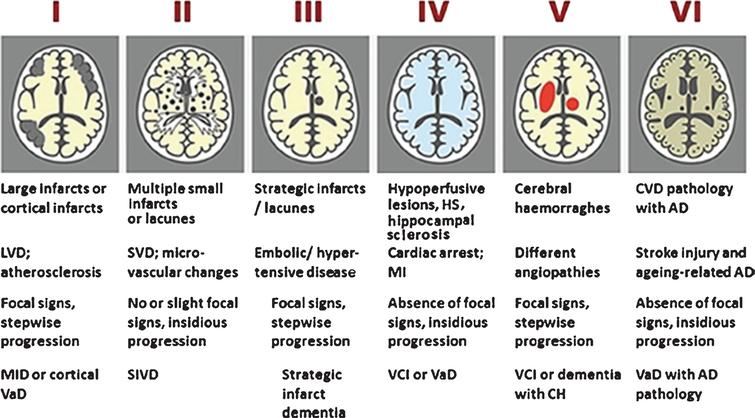
Small Vessel Cerebral Disease
Small vessel cerebral disease. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD accounts for the vast majority of non-traumatic spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage ICH accounting for 77 in patients aged 70 years or younger in a study from Western Europe1 and 7785 of patients aged 18 years or older in a study from Western Europe and the USA2 Meta-analyses3 of randomised controlled trials suggest that oral. Cerebral small vessel diseases are responsible for 20-30 of ischemic strokes as well as for a considerable proportion of cerebral hemorrhages and encephalopathies. In general the relations are weak and not all subjects with SVD become demented or get parkinsonism.
Thechanges affect arterioles capillaries and small veins supplying the white matter and deep structures ofthebrain. Itis themost common incidental finding onbrain scans especially in. Cerebral small vessel disease CSVD is composed of several diseases affecting the small arteries arterioles venules and capillaries of the brain and refers to several pathological processes and etiologies.
Our network which links clinical and preclinical research across North America and Europe aims to address this. Cerebral smallvessel disease cohort studies incident depression metaanalysis. Cerebral smallvessel disease features such as WMHs enlarged perivascular spaces and cerebral atrophy especially the severity of WMHs and deep WMHs are risk factors for incident depression.
SVD can also be caused by a stroke. The changes affect arterioles capillaries and small veins supplying the white matter and deep structures of the brain. In 1999 the Rotterdam Scan Study found that of 1077 people ages 60 to 90 more than 90 percent showed evidence of cerebral small vessel disease.
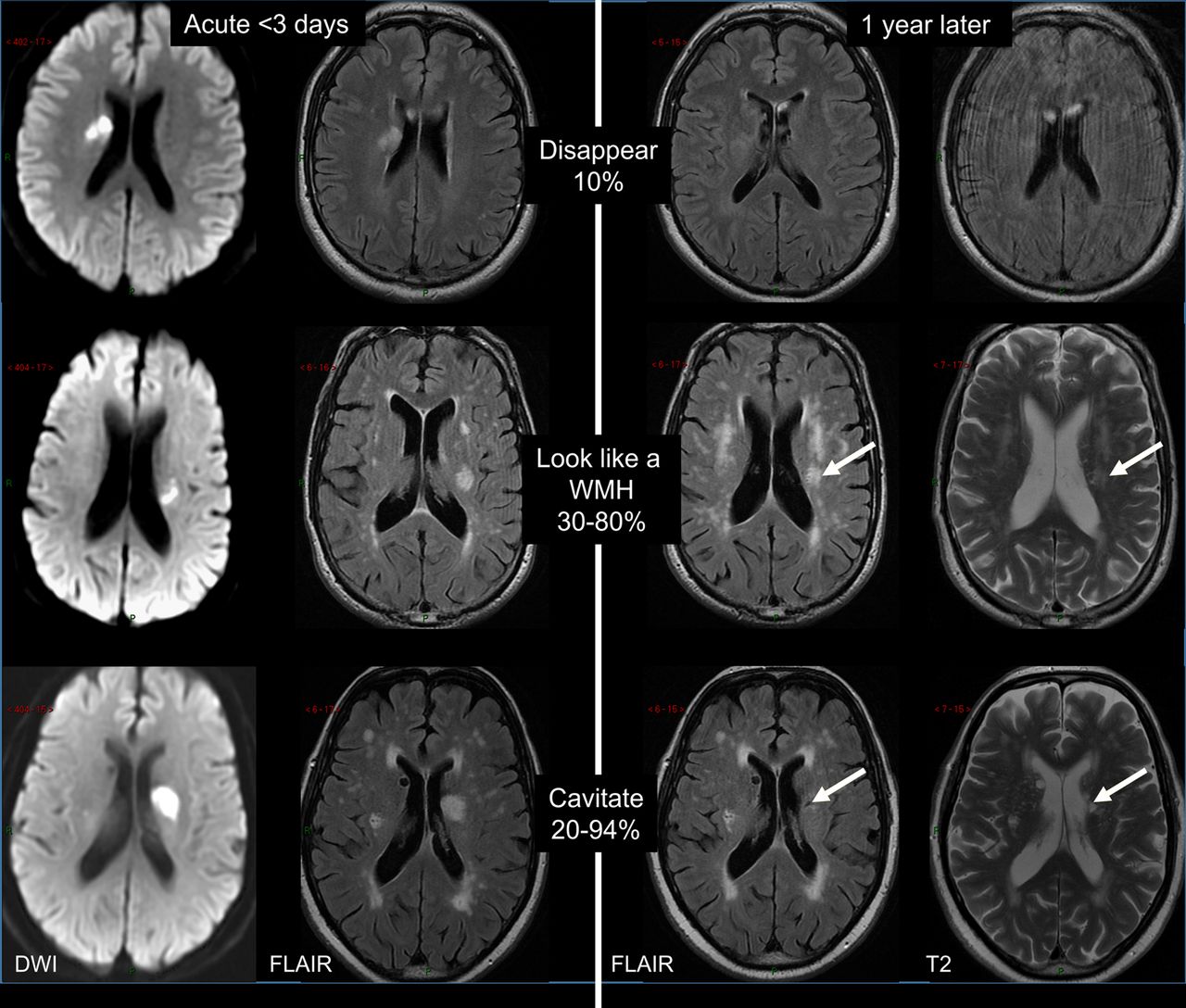
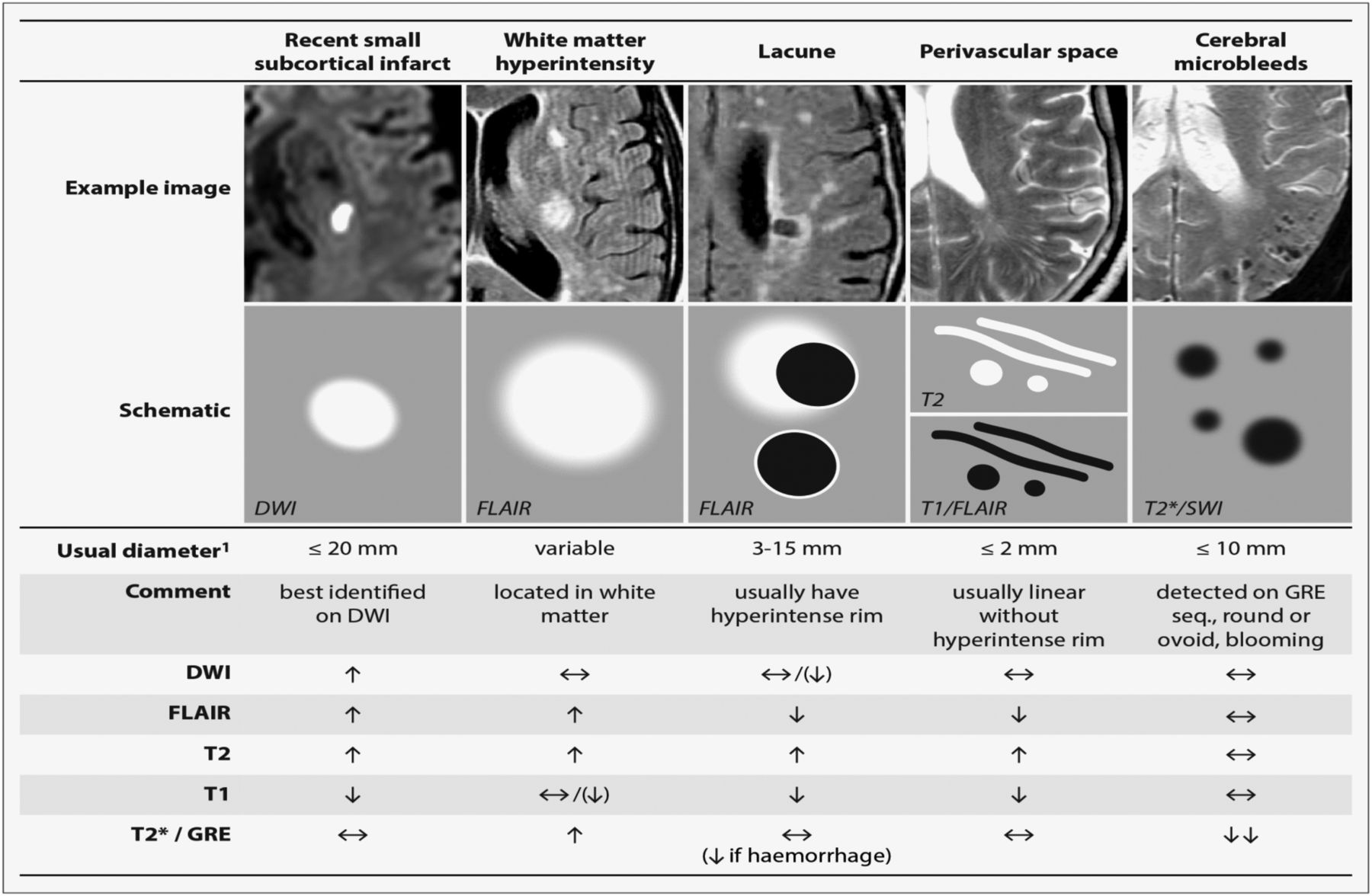
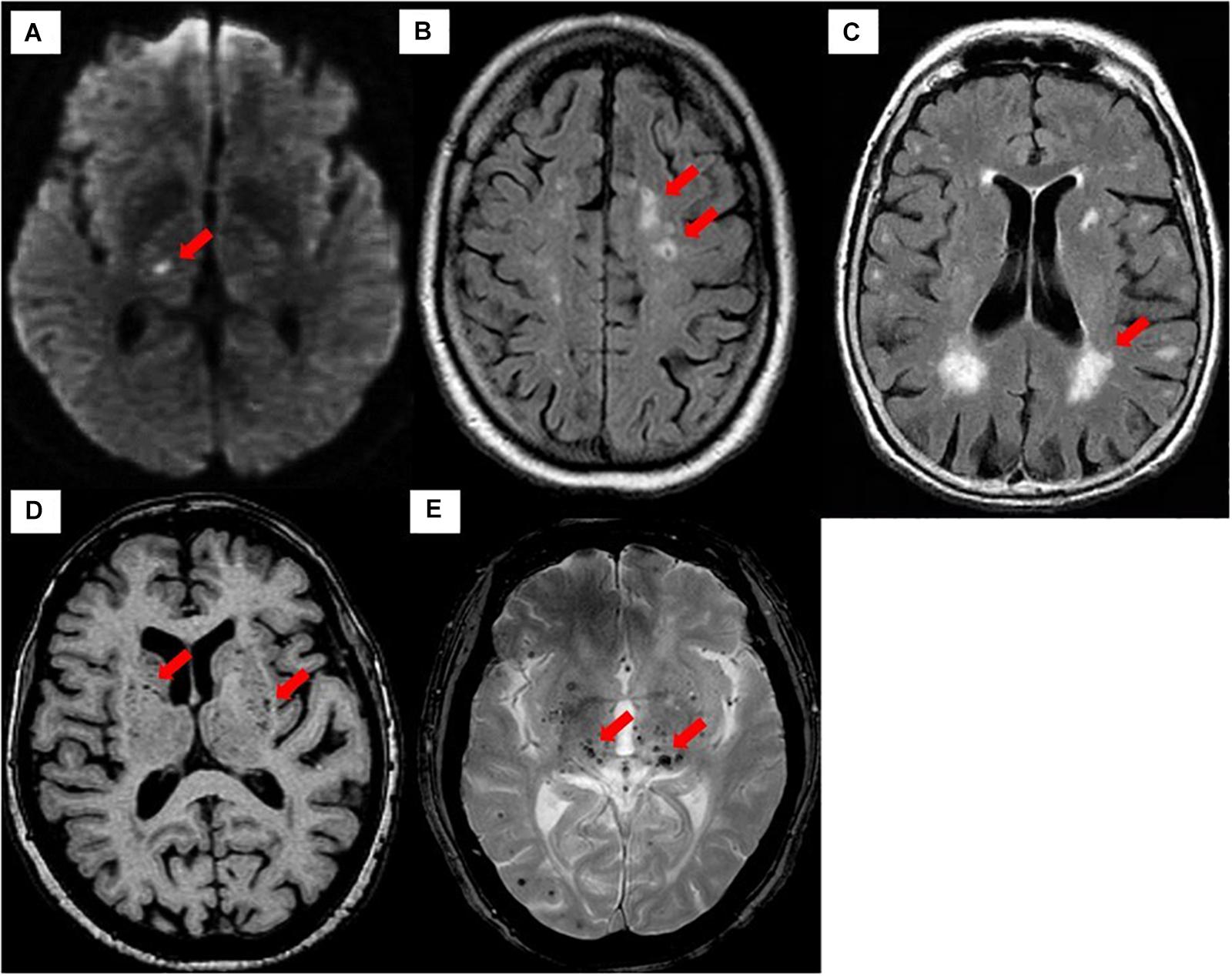
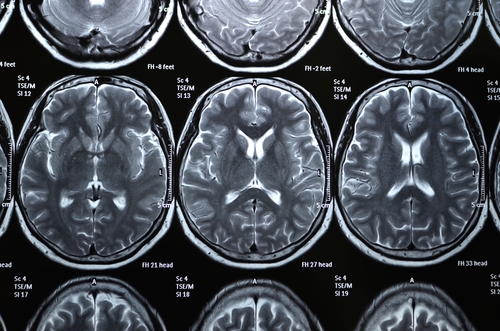
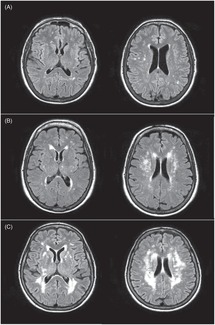
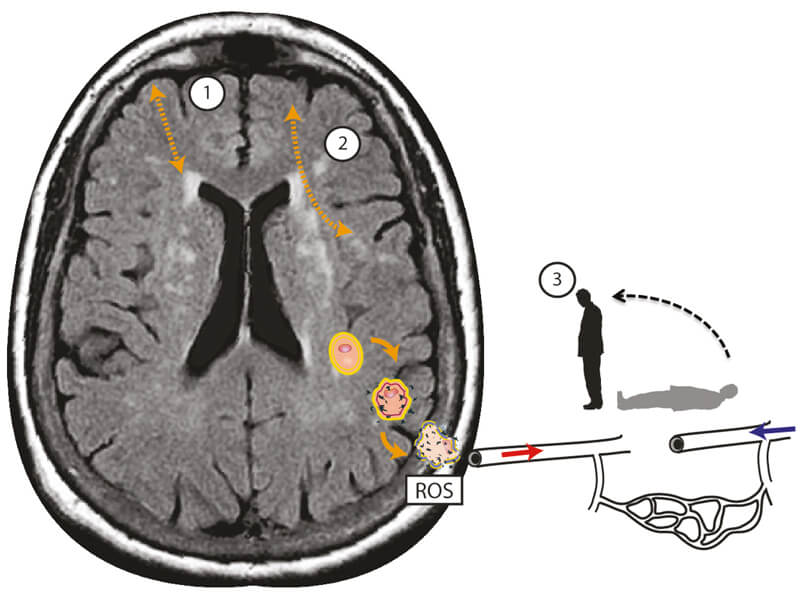
As such SVD is the underlying pathology responsible for manifestations that are both common and. This damage eventually affects the brain matter which is diagnosed with an MRI or CT. Small vessel disease is a disorder of cerebral microvessels that causes white matter hyperintensities and several other common abnormalities eg recent small subcortical infarcts and.
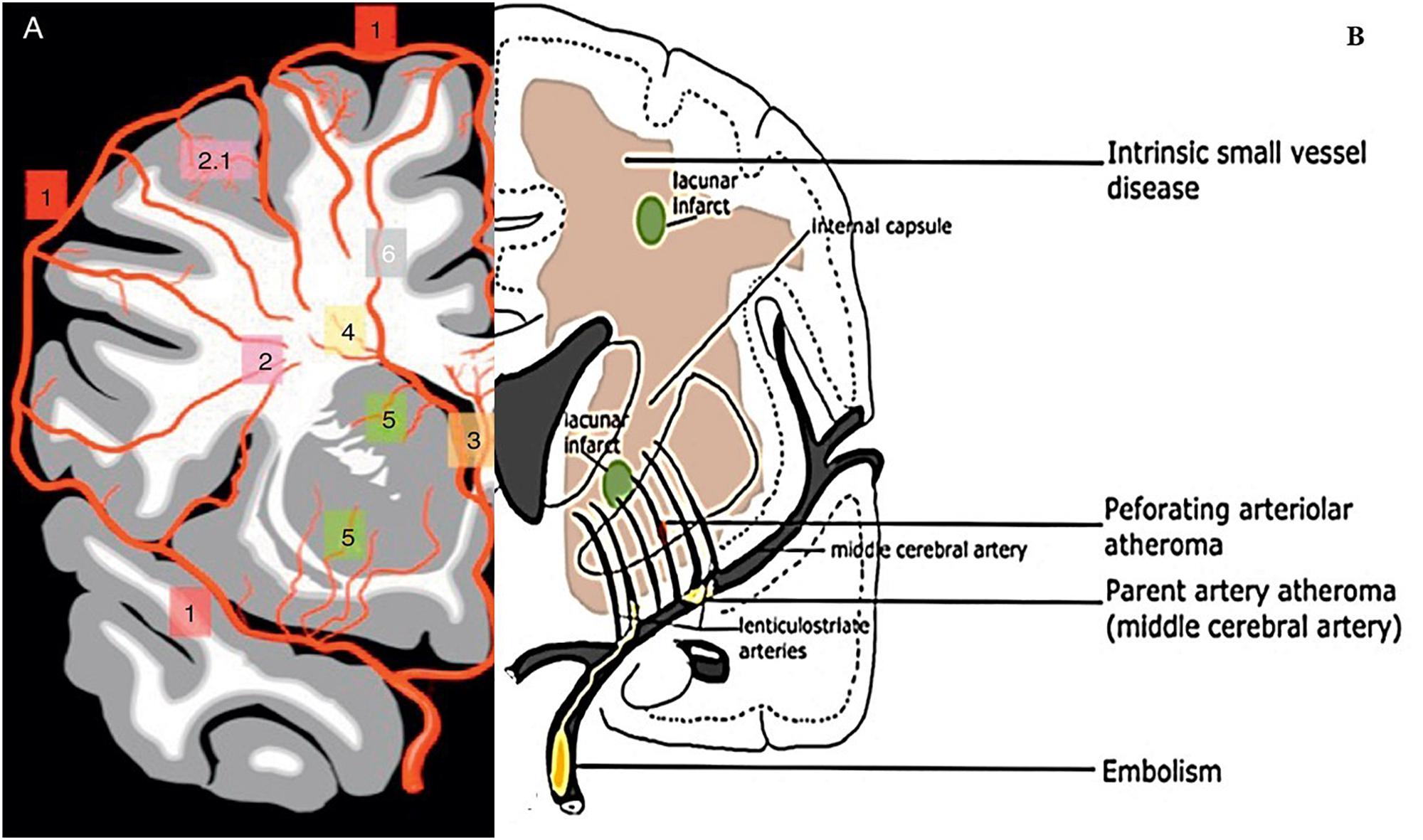
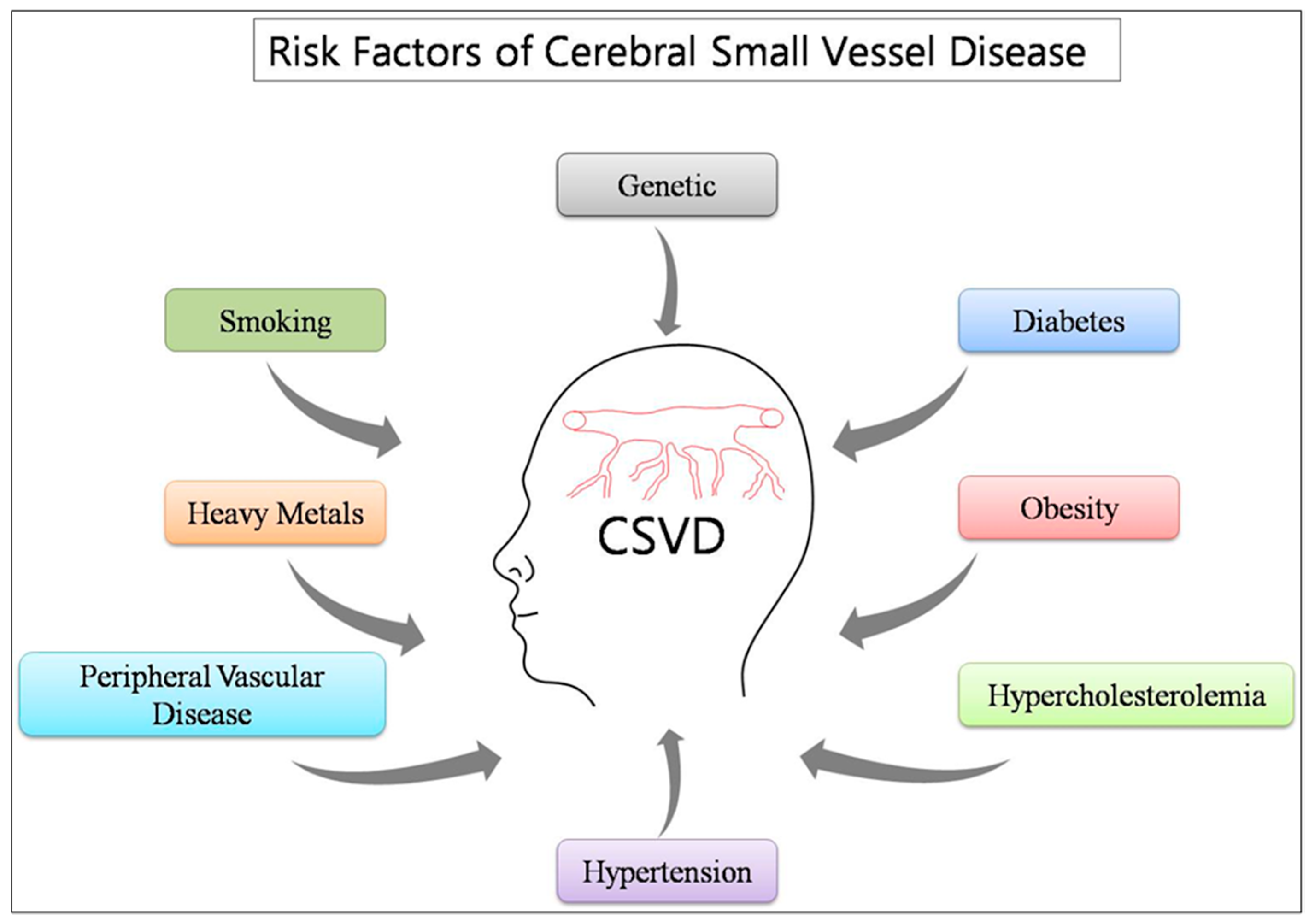
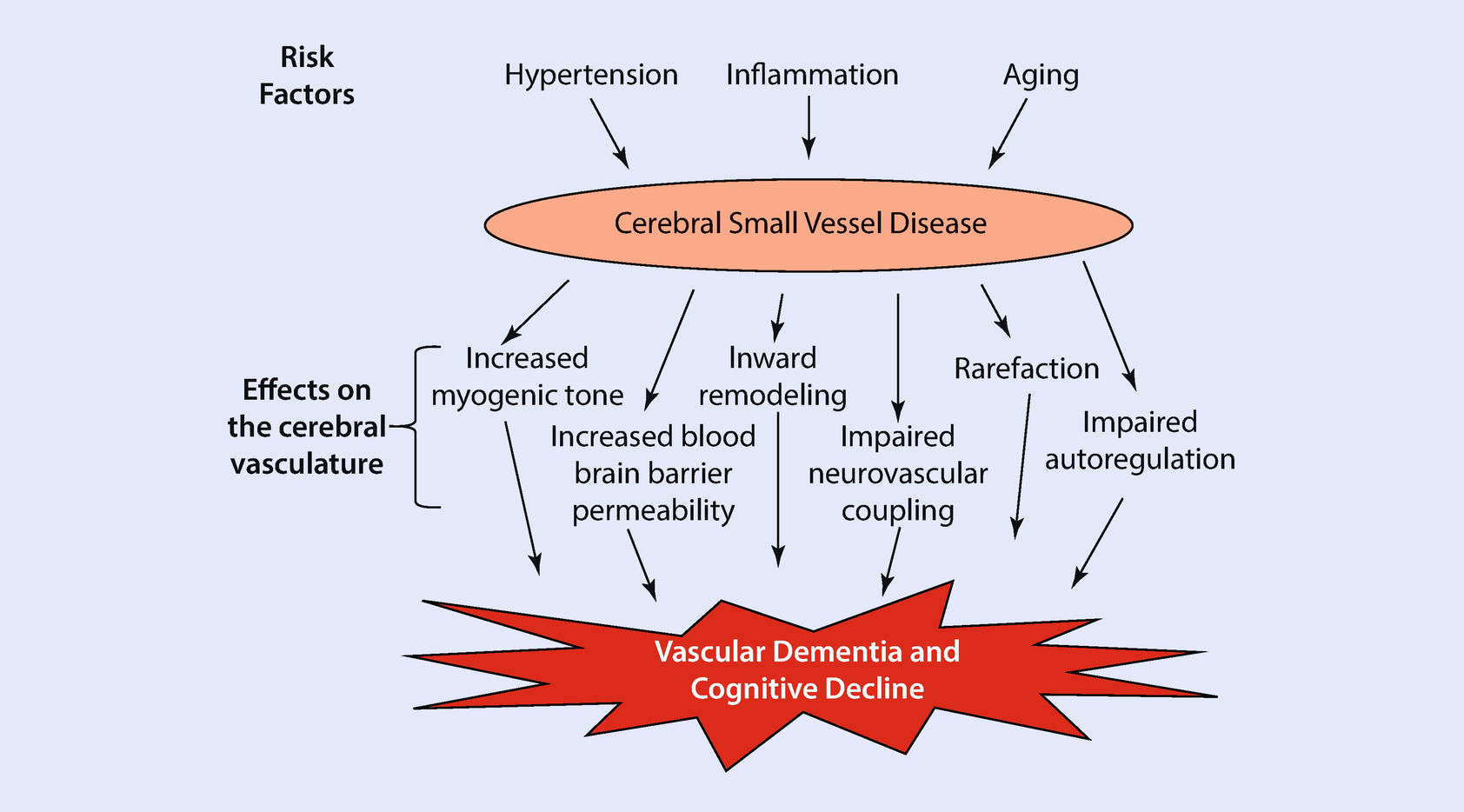
Cerebral small vessel disease SVD includes pathology of the brains small arteries arterioles capillaries venules and veins1 Key risk factors for SVD include age and cardiovascular risk factors23 although vascular risk does not fully account for SVD pointing to its multifactorial nature and as of yet unclear underlying mechanism. Cerebral small vessel disease CSVD is the most common chronic and progressive vascular disease. It causes damage within the brain which shows up on brain scans as small changes on brain scans called lesions.
Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is an umbrella term covering a variety of abnormalities related to small blood vessels in the brain. Cerebral small vessel disease is one of the most common neurological disorders of agingnearly all of us develop some form of the disease as we get older.
It causes damage within the brain which shows up on brain scans as small changes on brain scans called lesions.
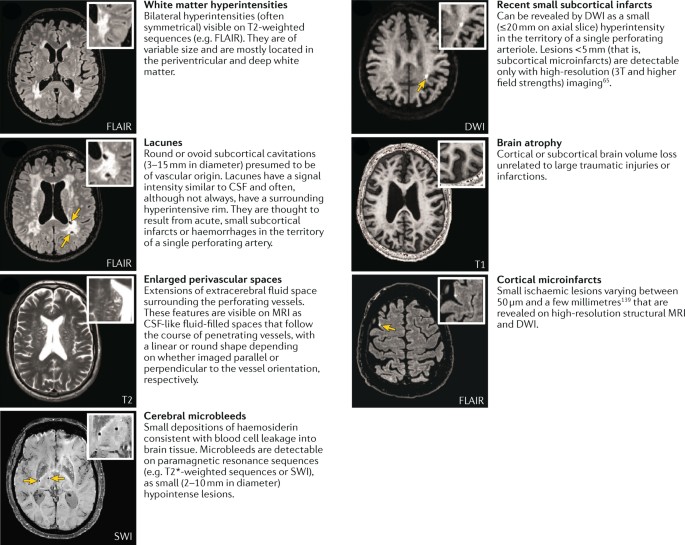
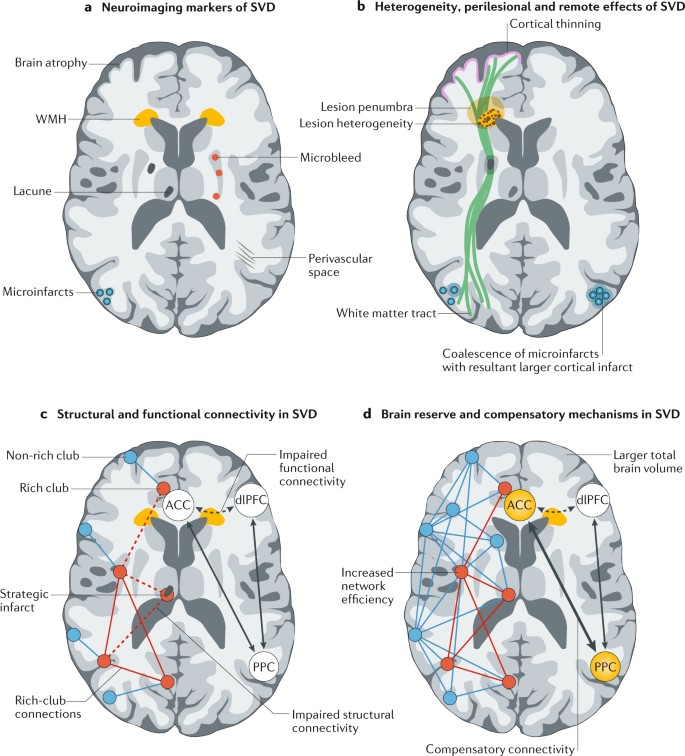
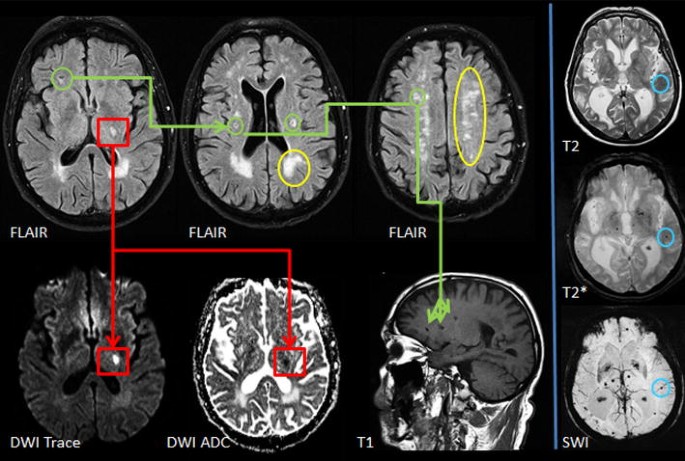
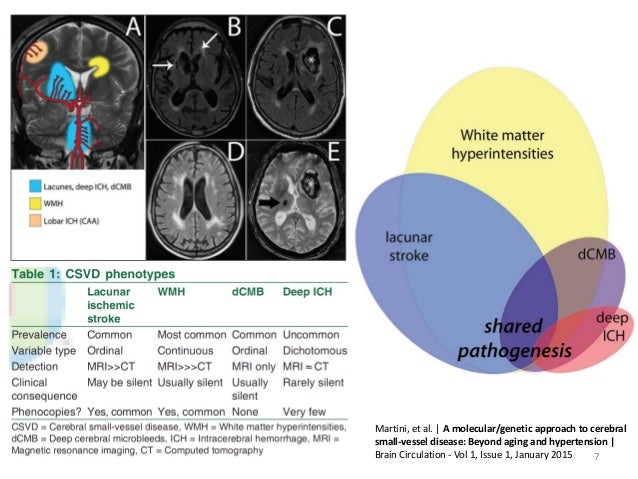
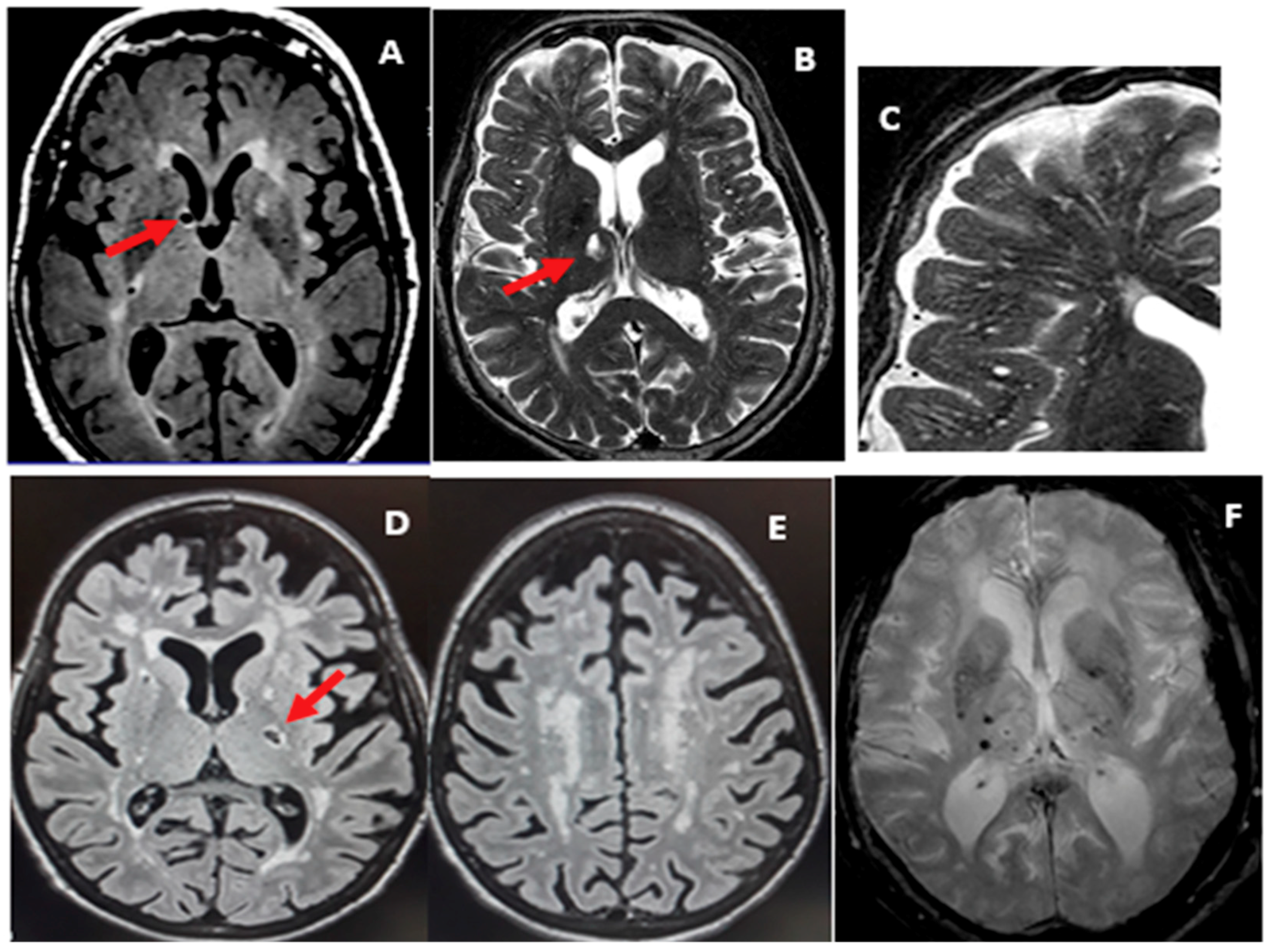
It causes damage within the brain which shows up on brain scans as small changes on brain scans called lesions. Cerebral small vessel disease CSVD is the most common chronic and progressive vascular disease. SVD is thought to cause around a quarter of strokes. Small ischemic vessel disease occurs when there is damage to either the vessels themselves or the surrounding white brain matter. As such SVD is the underlying pathology responsible for manifestations that are both common and. Fondation Leducq have funded an international network to investigate the role of the perivascular space in cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimaging features of CSVD include recent small subcortical infarcts lacunes white m. Cerebral small vessel disease CSVD is composed of several diseases affecting the small arteries arterioles venules and capillaries of the brain and refers to several pathological processes and etiologies. In spite of distinctive pathogenesis CSVD shares similar neuroimaging markers including recent small su.
Cerebral small vessel disease is one of the most common neurological disorders of agingnearly all of us develop some form of the disease as we get older. We present recent developments in the field of small vessel disease SVD-related vascular cognitive impairment including pathological mechanisms updated diagnostic criteria cognitive profile neuroimaging markers and risk factors. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is a frequent finding on CT and MRI scans of elderly people and is related to vascular risk factors and cognitive and motor impairment ultimately leading to dementia or parkinsonism in some. Cerebral small vessel diseases are responsible for 20-30 of ischemic strokes as well as for a considerable proportion of cerebral hemorrhages and encephalopathies. Less known than the manifestations in old age are those in young women comprising posterior encephalopathy and. As such SVD is the underlying pathology responsible for manifestations that are both common and. Neuroimaging features of CSVD include recent small subcortical infarcts lacunes white m.





























Post a Comment for "Small Vessel Cerebral Disease"