Scleroderma Lung Disease Mortality
Scleroderma lung disease mortality. Patient status was determined at 31 December 1997. This review summarizes morbidity and mortality outcomes in SSc-ILD patients from high-quality observational and interventional studies over the last 50 years. Lung Diseases Interstitialetiology Lung Diseases Interstitialmortality.
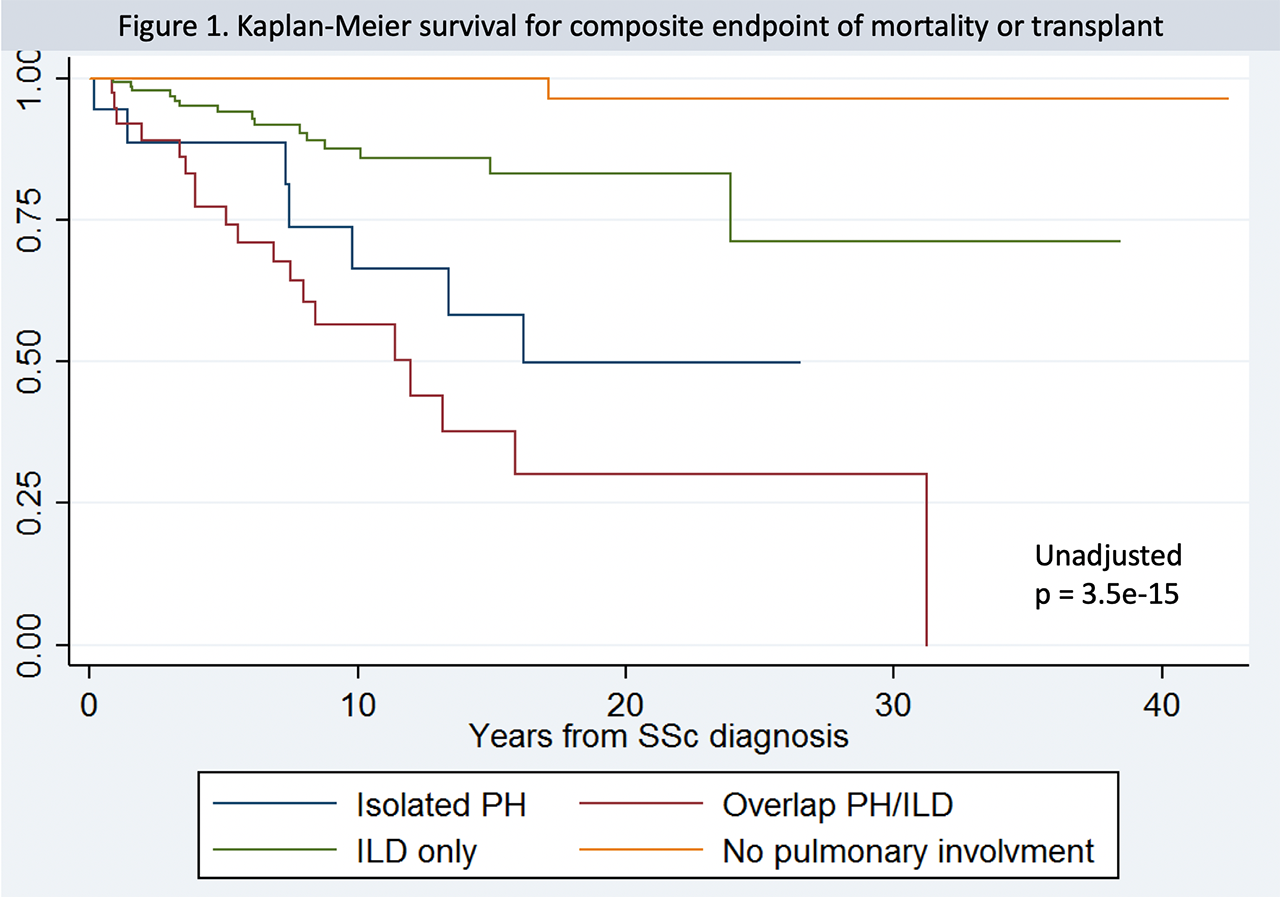
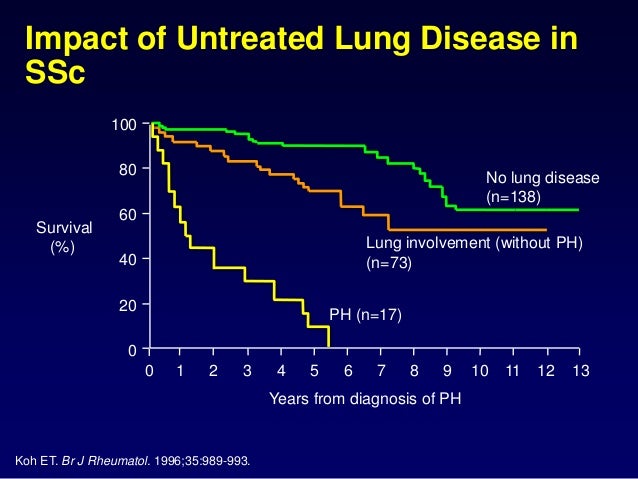
Hypertension PH and interstitial lung disease ILD is common in scleroderma and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality12 The prevalence of ILD in scleroderma is high and has been reported to occur in up to 90 of patients3 ILD is the most frequent cause of death among patients with scleroderma1. I have SSc with mild ILD and have been on Cellcept for 3 years. We conducted a systematic review to identify variables that predict mortality.
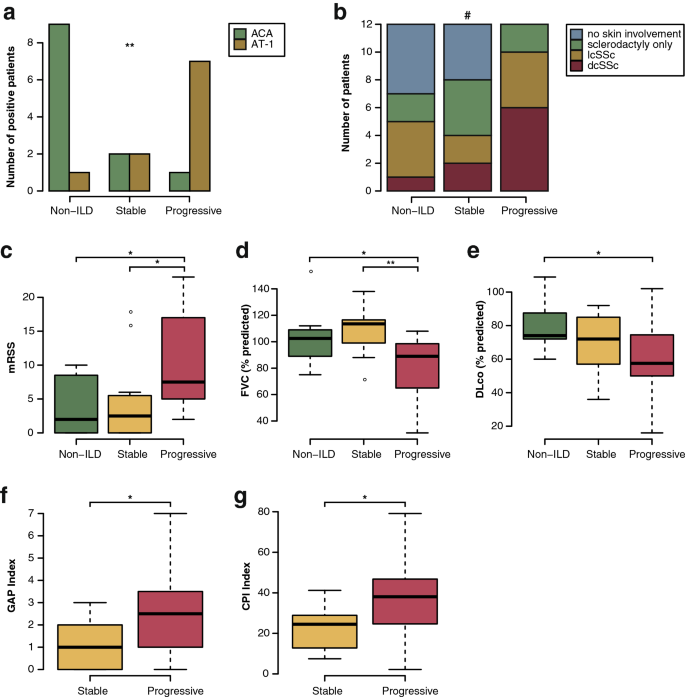
The lungs are involved in around 80 of all patients with scleroderma. Contemporary studies of systemic sclerosis consistently demonstrate that interstitial lung disease is a leading cause of disease-related death. Risk prediction and prognostication in patients with Scl-ILD are challenging because of heterogeneity in the disease course.
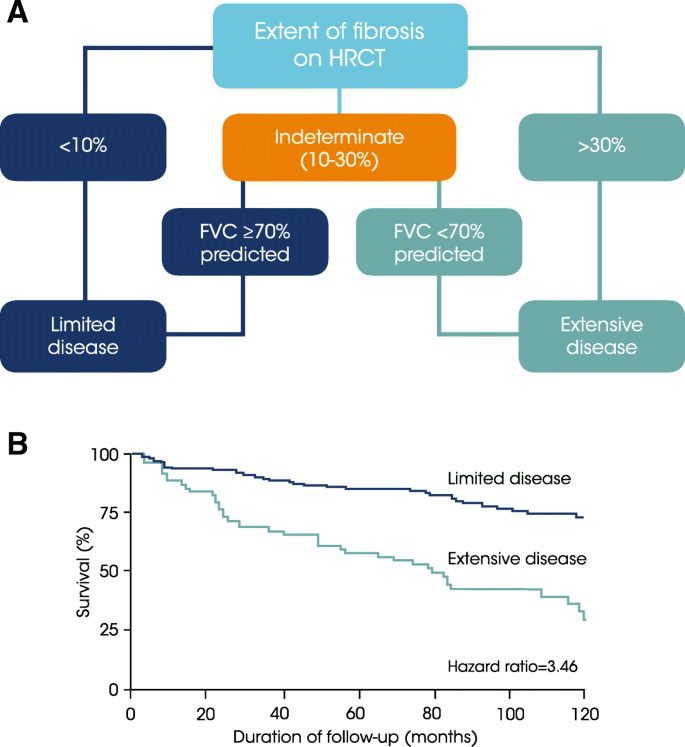
Scleroderma Systemiccomplications Scleroderma Systemicmortality. Average annual costs over the 5-year period ranged from 18513 to 23268 for patients with incident SSc from 31285 to 55446 for patients with incident SSc-ILD and from 44454 to 63320 for patients with incident SSc-PAH. A simple stratification that utilises pulmonary function tests PFTs and extent of disease on high-resolution computed tomography HRCT to provide discriminatory.
We conducted a systematic review to identify variables that predict mortality and ILD progression in SSc-ILD. Detailed clinical and laboratory assessments were undertaken at the initial visit. 3 ILD is the most frequent cause of death among patients with scleroderma.
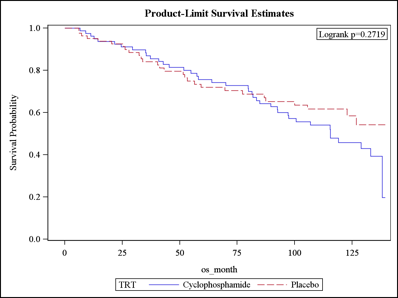
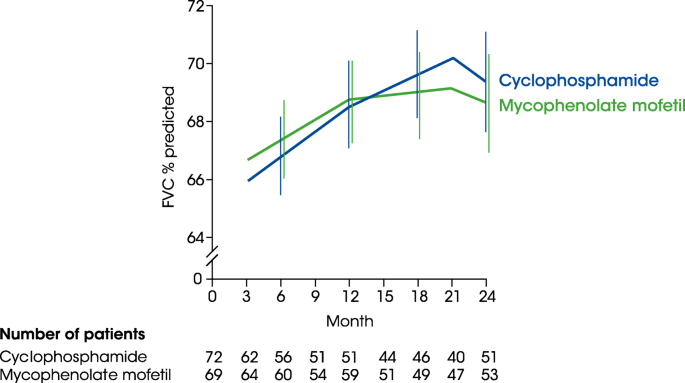
Scleroderma Lung Study I involved 158 patients with SSc-ILD who were randomly assigned to. Mortality associated with scleroderma renal crisis has declined significantly during the last decades as use of angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors. Lung Diseases Interstitialpathology Predictive Value of Tests.
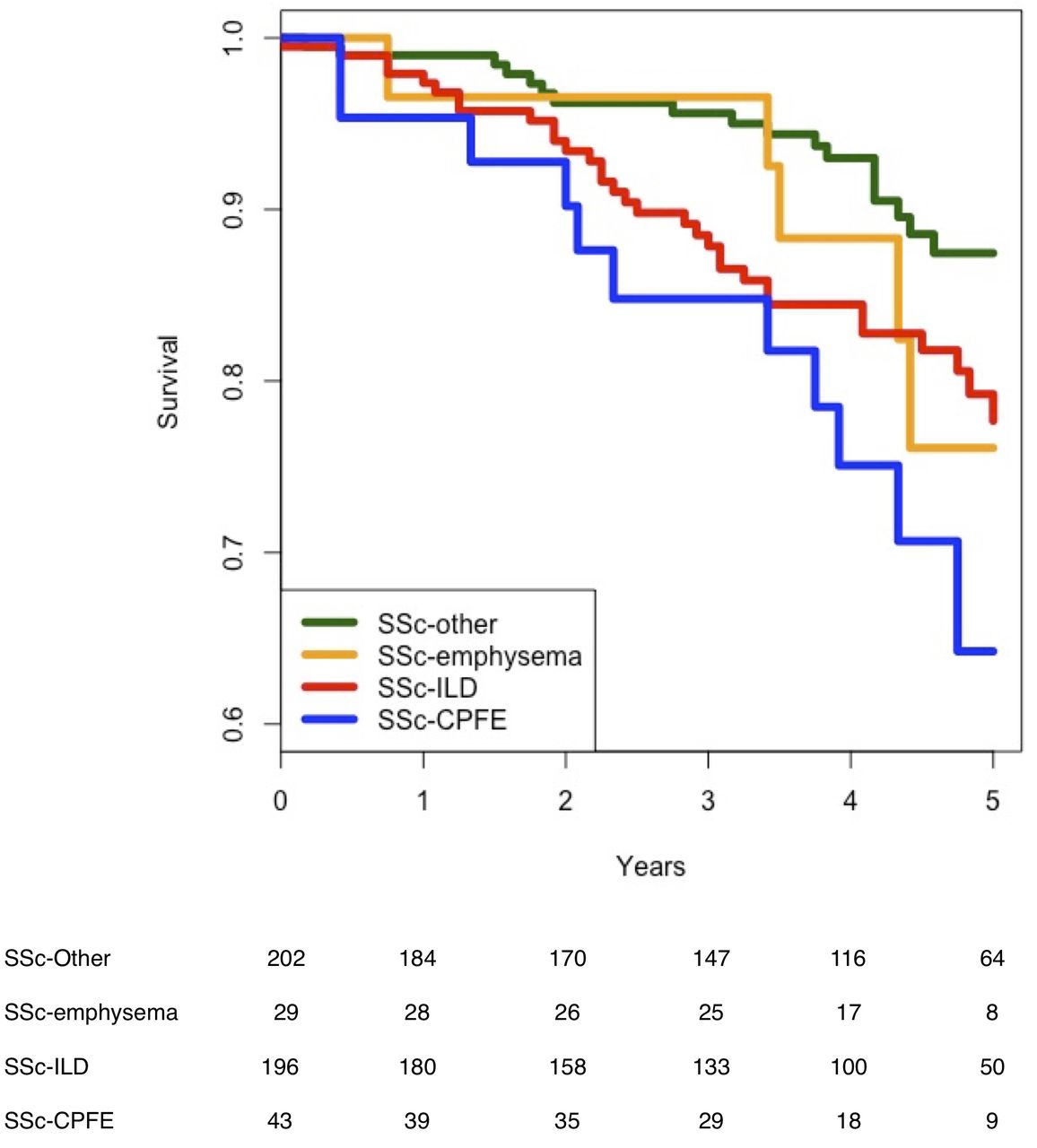
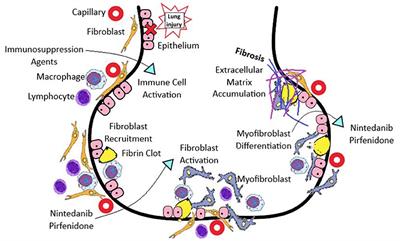
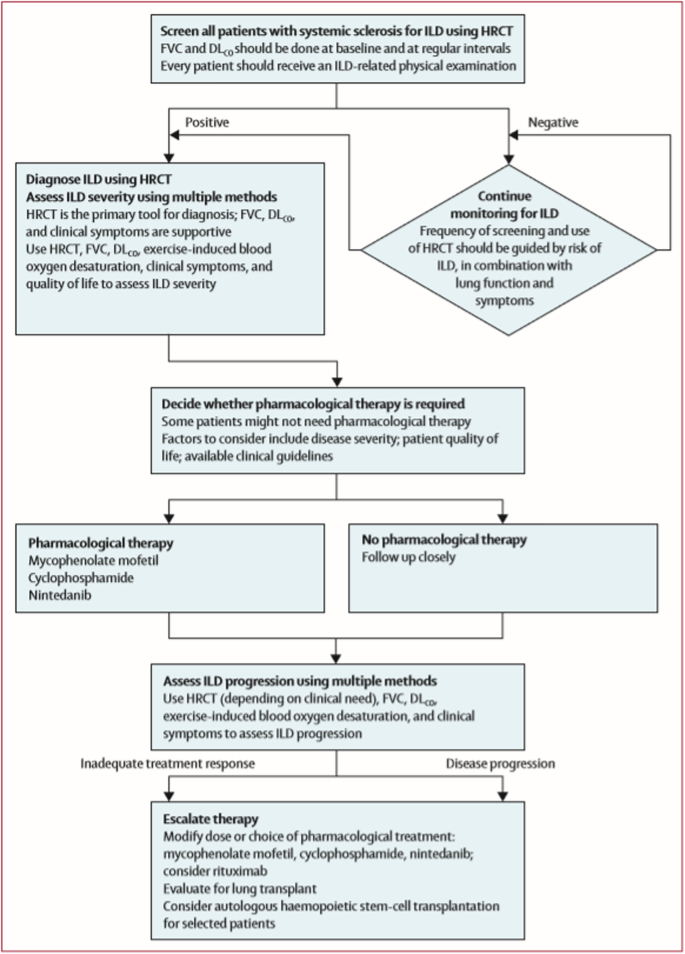
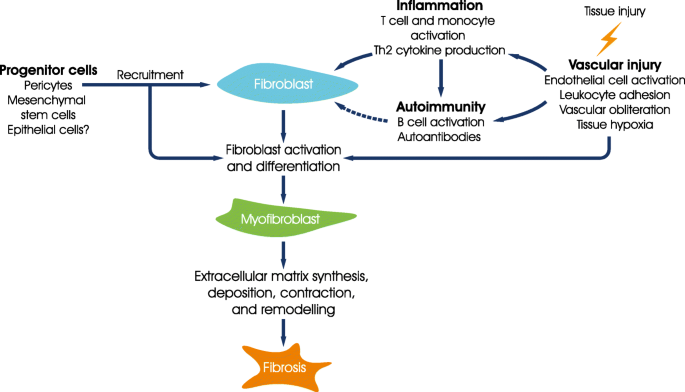
Because of this fact alone understanding the type of lung involvement and its level of activity and severity forms the central information about treatment decisions. Pulmonary complications such as interstitial lung disease ILD and pulmonary hypertension contribute significantly to mortality and morbidity of the disease.
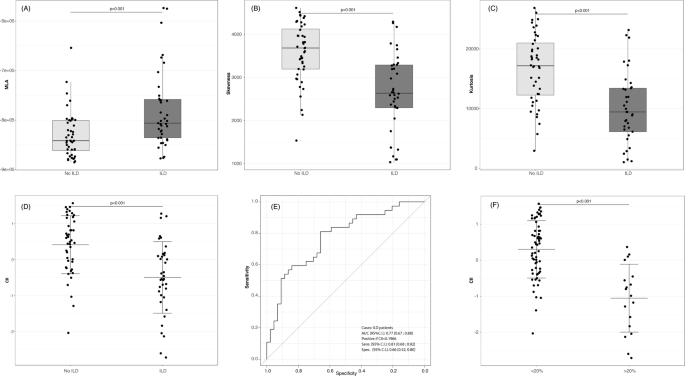
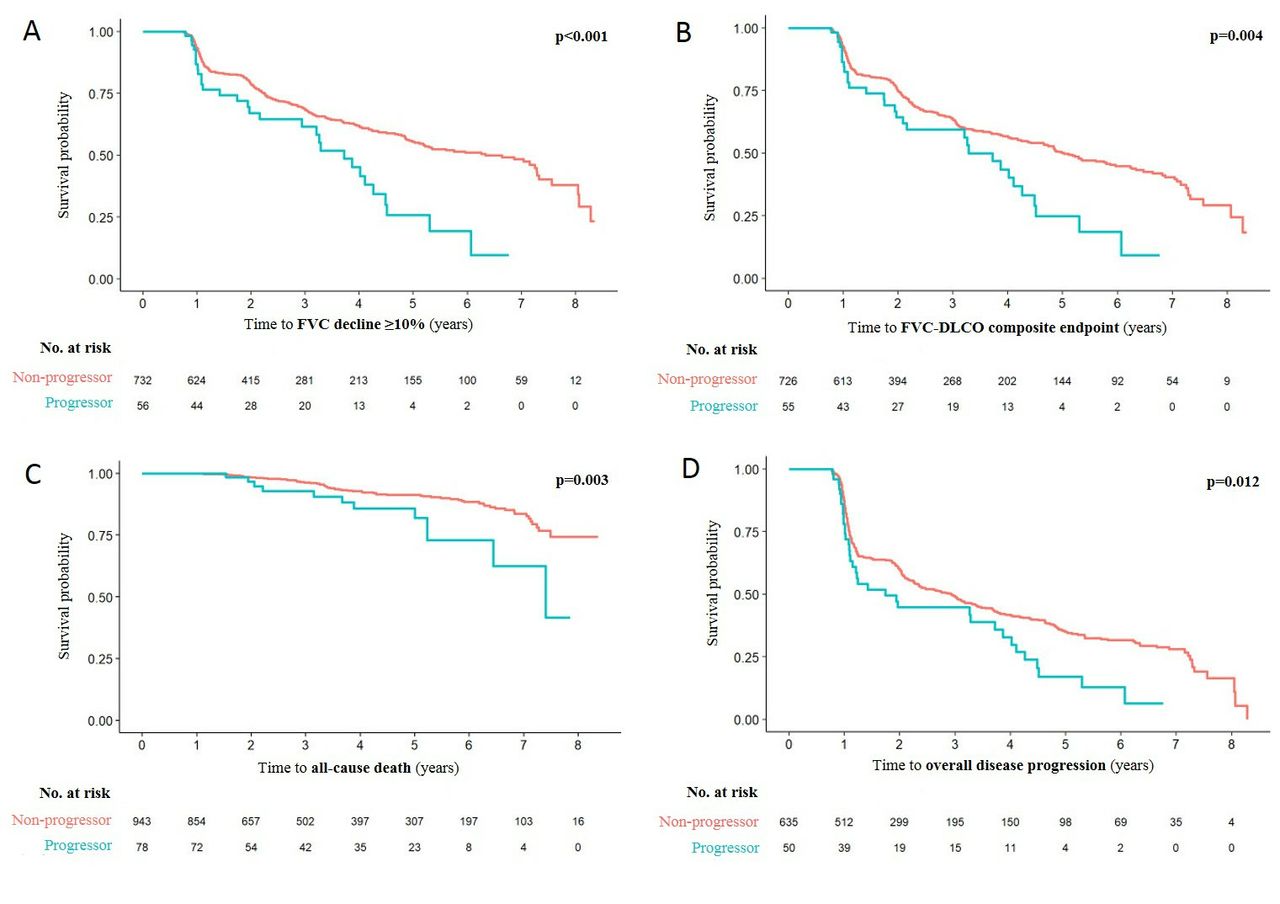
Extent of ILD Progression as a Surrogate for Mortality.
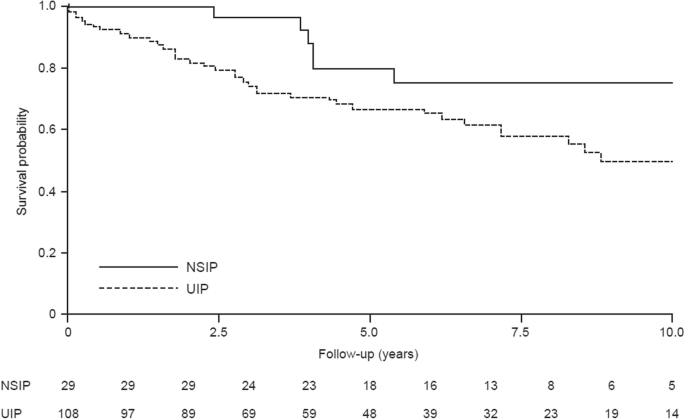
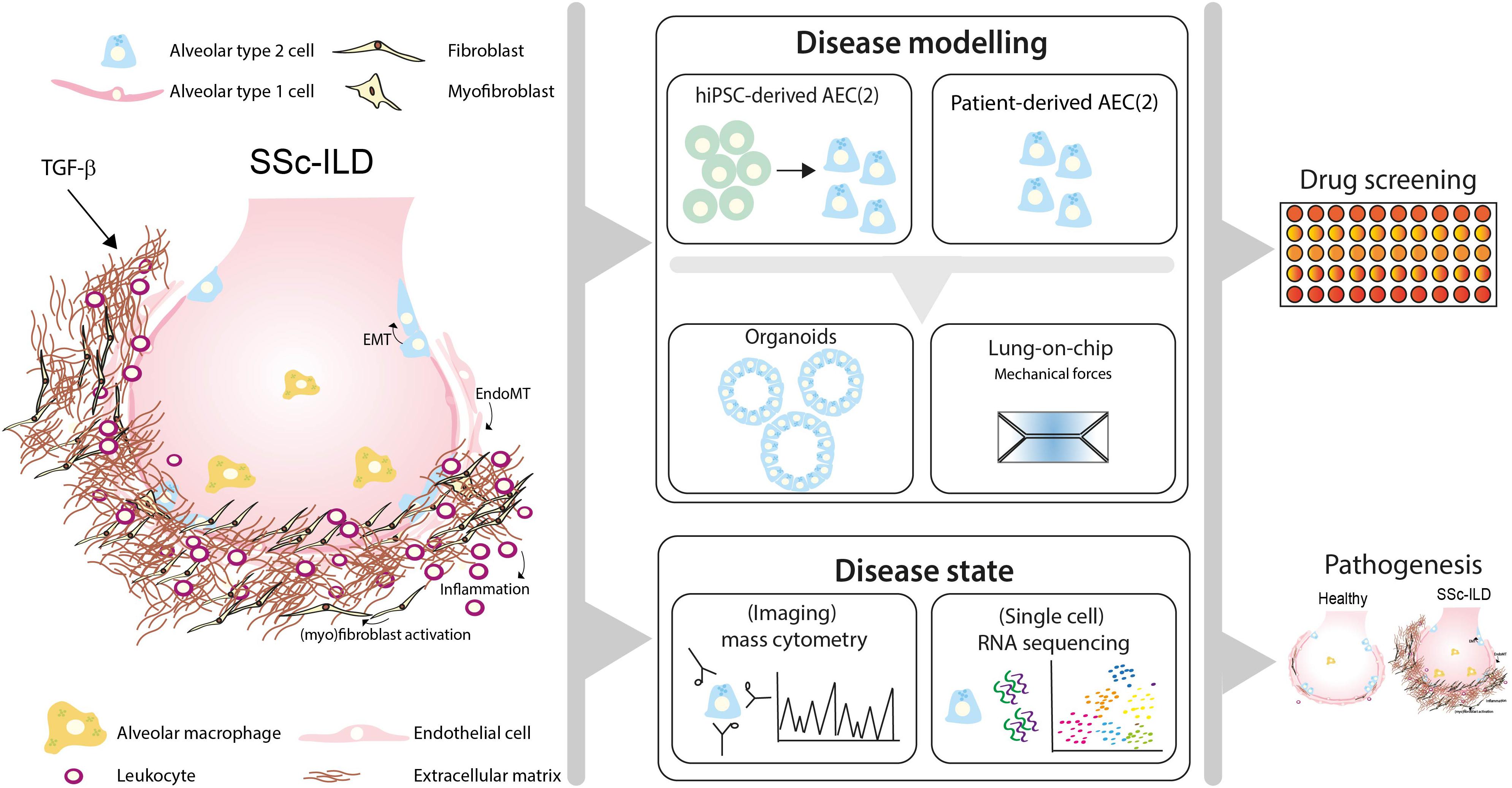
A simple stratification that utilises pulmonary function tests PFTs and extent of disease on high-resolution computed tomography HRCT to provide discriminatory. Contemporary studies of systemic sclerosis consistently demonstrate that interstitial lung disease is a leading cause of disease-related death. Scleroderma SSc is an autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy and fibrosis with multi organ involvement. A simple stratification that utilises pulmonary function tests PFTs and extent of disease on high-resolution computed tomography HRCT to provide discriminatory. The lungs are involved in around 80 of all patients with scleroderma. However prognostication of SSc-associated ILD SSc-ILD remains challenging. Lung Diseases Interstitialpathology Predictive Value of Tests. Mortality rates at three years were 14 and at 24 at six years for patients presenting three of those. Pulmonary complications such as interstitial lung disease ILD and pulmonary hypertension contribute significantly to mortality and morbidity of the disease.
While virtually any organ system may be involved in the disease process fibrotic and vascular pulmonary manifestations of SSc including inter-stitial lung disease ILD and pulmonary hypertension PH are the leading cause of death. This review summarizes morbidity and mortality outcomes in SSc-ILD patients from high-quality observational and interventional studies over the last 50 years. Age at disease onset older than 45 male gender having diffuse scleroderma pulmonary fibrosis pulmonary hypertension and a DLCO a measure of lung function lower than 60. However prognostication of SSc-associated ILD SSc-ILD remains challenging. Pulmonary involvement including pulmonary hypertension PH and interstitial lung disease ILD is common in scleroderma and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality1 2 The prevalence of ILD in scleroderma is high and has been reported to occur in up to 90 of patients. Contemporary studies of systemic sclerosis consistently demonstrate that interstitial lung disease is a leading cause of disease-related death. Scleroderma SSc is an autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy and fibrosis with multi organ involvement.
































Post a Comment for "Scleroderma Lung Disease Mortality"