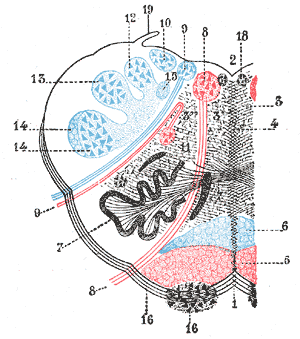
Lateral Medullary Syndrome Mri
Lateral medullary syndrome mri. Ross MA Biller J Adams HP Jr Dunn V. Four patients with a clinical diagnosis of Wallenbergs lateral medullarysyndrome were studied with both Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI and cranialComputed Tomography CT. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI brain stem ischemic strokes can be more definitivel1-2 y evaluated.
Most commonly due to an occlusion of the intracranial portion of the vertebral artery followed by PICA and its branches. Lateral medullary syndrome also known as Wallenberg syndrome is a clinical syndrome caused by an acute ischemic infarct of the lateral medulla oblongata. It is usually secondary to the vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery occlusion due to atherothrombosis or embolism and also due to a spontaneous dissection of the vertebral arteries 1-3.
Ross et al3 found MRI-identified lesions in their 4 patients with lateral medullary syndrome LMS and Bogouss-lavsky et al4 described 6 patients who had small verte-brobasilar territory infarcts with good clinical-MRI corre-lation. Lateral medullary syndrome LMS or Wallenberg syndrome is a brainstem infarction that presents as a clinical syndrome with typical neurological symptoms and signs because of its location 1. According to a study the highest incidence is seen in middle-aged males at 50-60 years.
Correlation between clinical findings and magnetic resonance imaging in 33 subjects. Lateral medullary syndrome is more common. Although lateral medullary infarction is a relatively common type of cerebrovascular disease detailed correlation between clinical findings and magnetic resonance imaging MRI has not yet been reported.
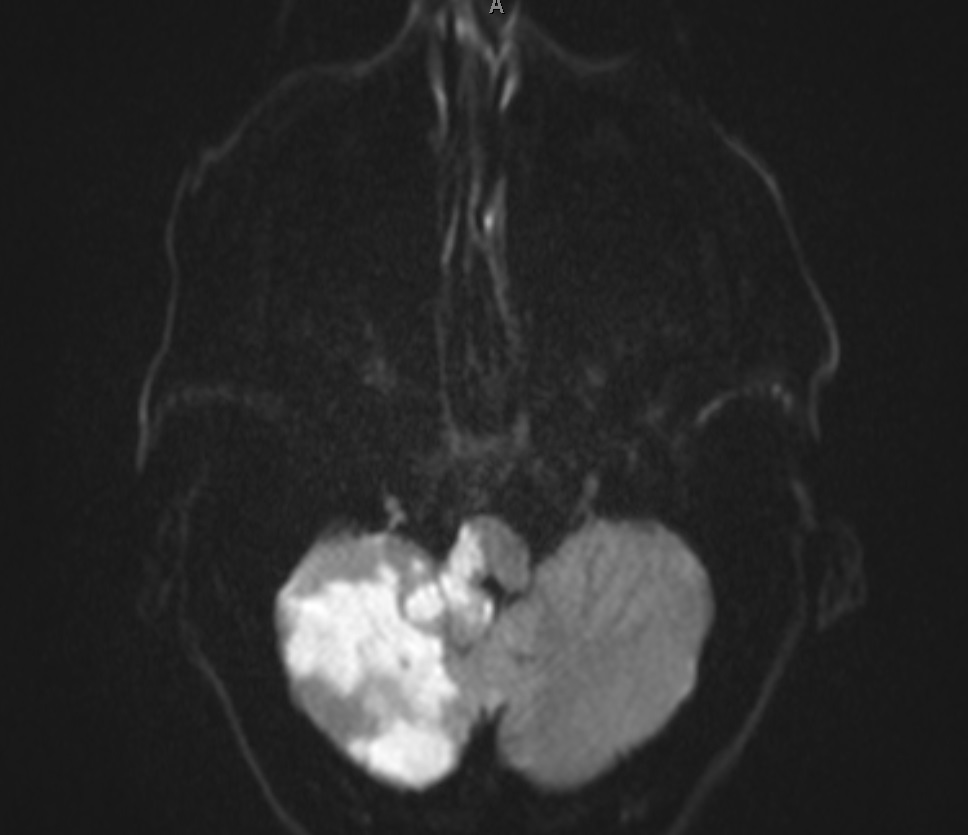
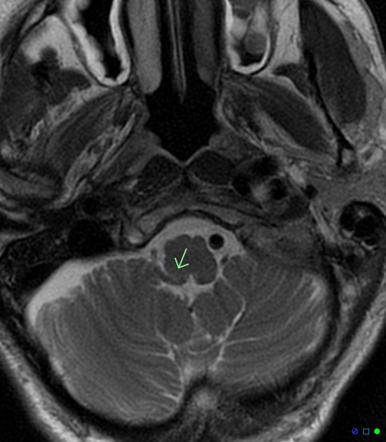
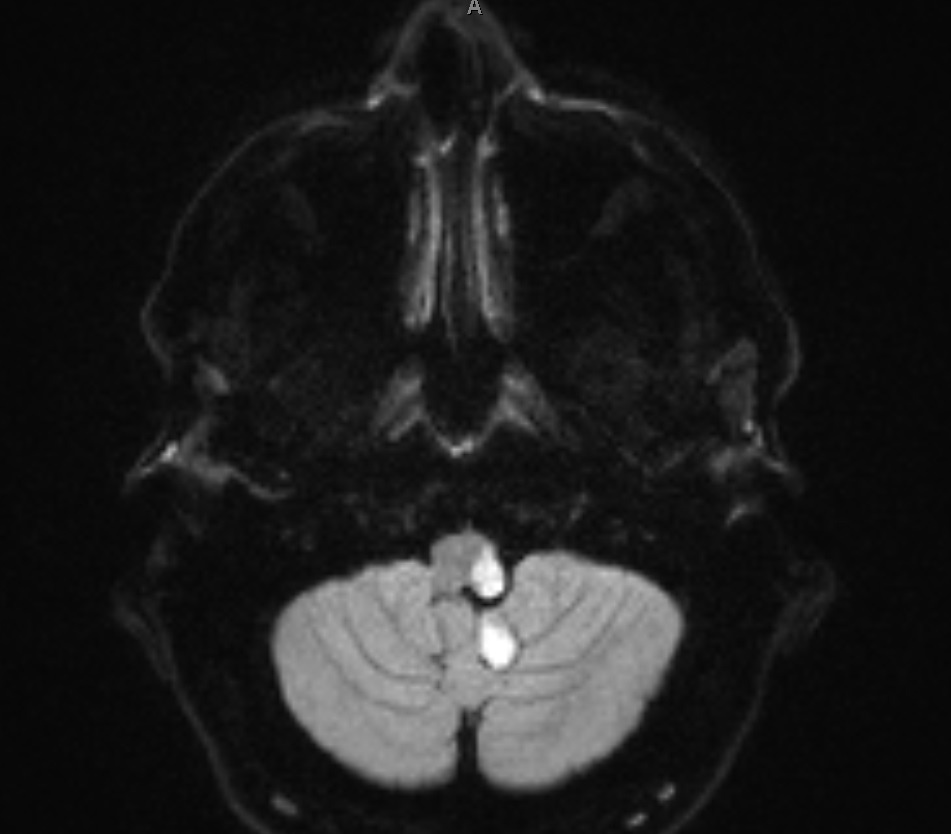
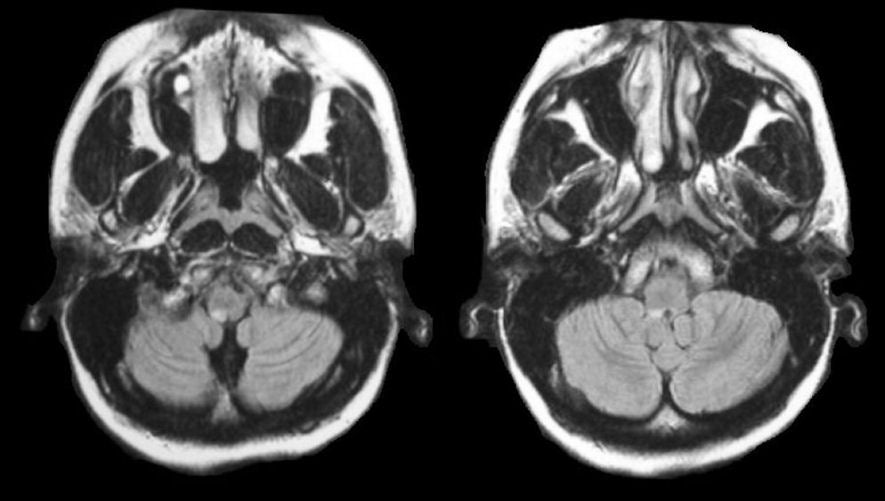
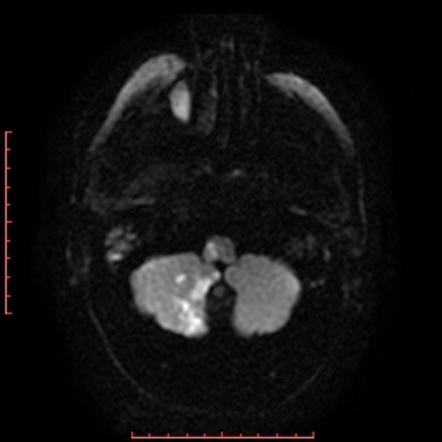
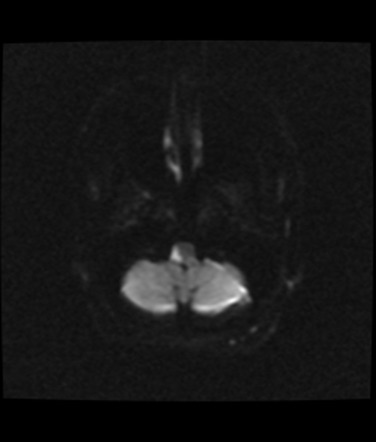
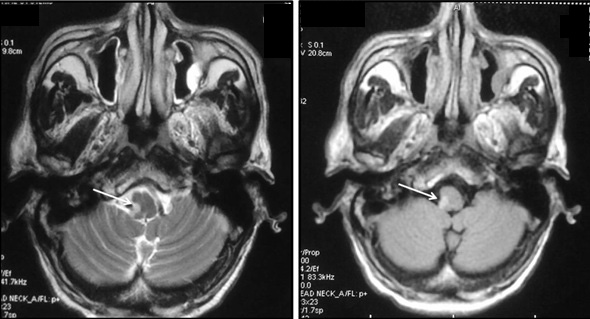
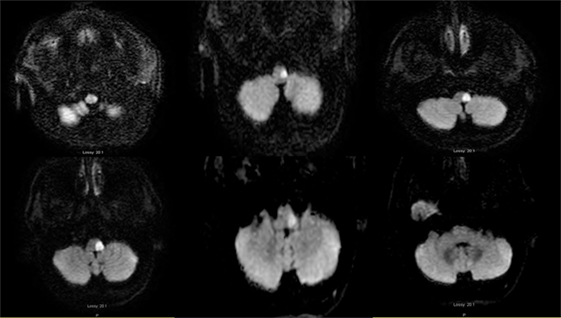
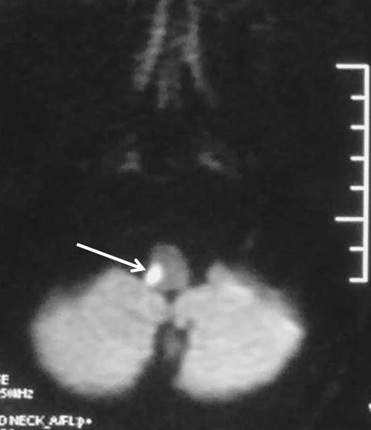
Using transverse images and both T1 and T2--weightedsequences MRI demonstrated a medullary infarction. Using transverse images and both Tand T2 weighted sequences MRI demonstrated a medullary infarction not seen on CT in all four cases. Clinical-magnetic resonance imaging correlations.
CAS Article Google Scholar 5. Kim JS Lee JH Suh DC Lee MC. Marie-Foix Syndrome Marie-Foix syndrome lateral pontine syndrome is caused by infarction of the lateral pons and middle cerebellar peduncle from occlusion of perforating branches of the basilar and anterior inferior cerebellar arteries.
This is most commonly due to occlusion of the intracranial portion of the vertebral artery followed by PICA and its branches 1-3. Using transverse images and both T1 and T2--weighted sequences MRI demonstrated a medullary infarction not seen on CT in all four cases.
According to a study the highest incidence is seen in middle-aged males at 50-60 years.
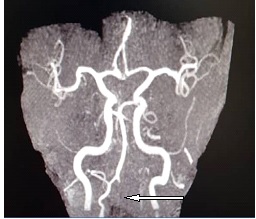
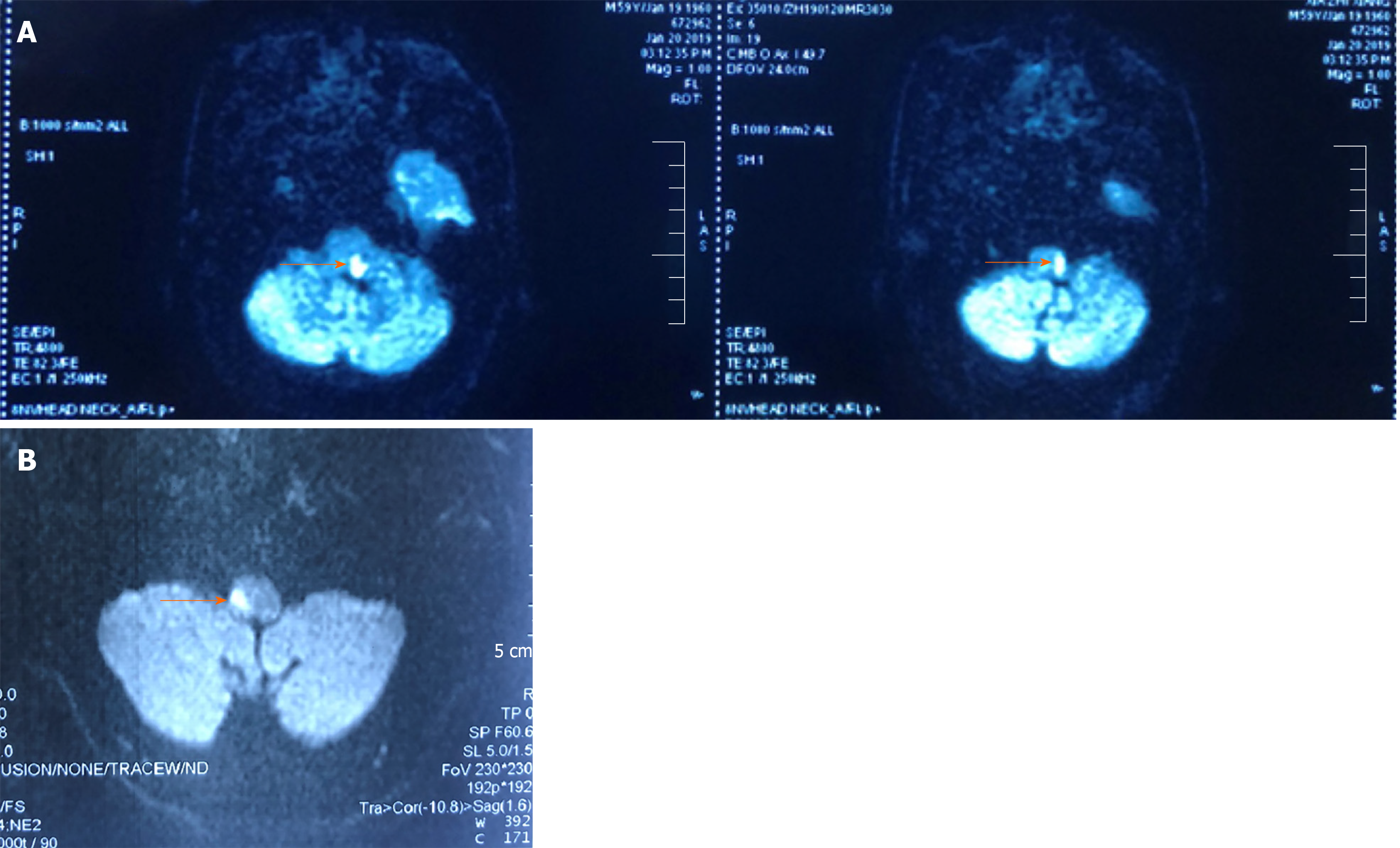
The syndrome results from infarction of the medulla by vertebral artery thrombosis or dissection that may also produce occlusion of the opening to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery33. Four patients with a clinical diagnosis of Wallenbergs lateral medullarysyndrome were studied with both Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI and cranialComputed Tomography CT. Hypertension diabetes smoking and atherosclerosis are the major risk factors. Marie-Foix Syndrome Marie-Foix syndrome lateral pontine syndrome is caused by infarction of the lateral pons and middle cerebellar peduncle from occlusion of perforating branches of the basilar and anterior inferior cerebellar arteries. Spectrum of lateral medullary syndrome. Most commonly due to an occlusion of the intracranial portion of the vertebral artery followed by PICA and its branches. The lateral medullary syndrome also known as Wallenbergs syndrome is the prototype lesion involving the nuclei of cranial nerves IX and X. Four patients with a clinical diagnosis of Wallenbergs lateral medullary syndrome were studied with both Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI and cranial Computed Tomography CT. MRI of the brain findings were notable for an acute left lateral medullary infarct Figure and CTA showed likely occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
SUMMARY Four patient a clinicas witl diagnosih of Wallenbergs s lateral medullary syndrome were studied with both Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI and cranial Computed Tomography CT. Ross MA Biller J Adams HP Jr Dunn V. Medial medullary syndrome is usually caused by infarction following vascular insult. This is most commonly due to occlusion of the intracranial portion of the vertebral artery followed by PICA and its branches 1-3. Using transverse images and both Tand T2 weighted sequences MRI demonstrated a medullary infarction not seen on CT in all four cases. Wallenberg syndrome Lateral medullary syndrome aka PICA syndrome Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery syndrome Constellation of neurologic symptoms due to injury to the lateral part of the medulla in the brain Sensory deficits affecting the trunk torso and. Spectrum of lateral medullary syndrome.































Post a Comment for "Lateral Medullary Syndrome Mri"